Principle
During an organism’s life, the relative concentration of carbon 14 in it is constant because of respiration, nutrition, photosynthesis or any other interaction with the biosphere. At its death, all exchanges stopping, the concentration of radioactive carbon-14 decreases due to a reduction by half every 5,570 years. Thus, determining the content of residual C14 dates the death of an organism.
Measurements
A fragment or a sample of some tens of milligrams (about 35 mg except for bones and ivory) is vaporized.
The concentration of carbon 14 is then determined using a mass spectrometer (which allows the separation of the atoms according to their mass and their valence), in comparison with standard measurements. In parallel, the combined measurement of carbon 13 (stable isotope of carbon) provides access to information about the diet of the dated organism. This is particularly important for marine organisms and their consumers.
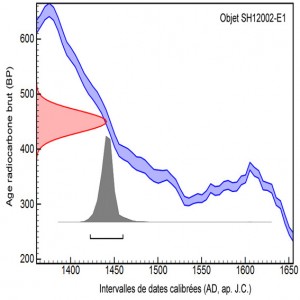
Calibration procedures and consideration of possible reservoir effects allow to transform the raw age into intervals of calendar dates.
Organic materials which compose objects of art can be dated using C14. However, depending on the problematics, other techniques can be used.
 |
 |
Download the document about Carbon 14 ![]()
Download the document about Carbon 14 for Archaeology (FRENCH) ![]()
Any question ? Any thought you would like to share ?
Contact us